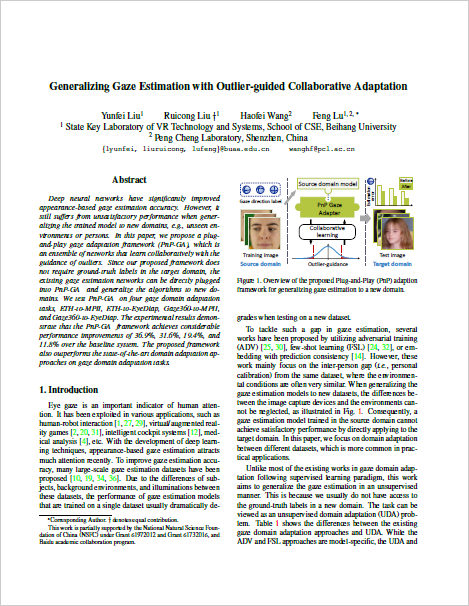
The Plug-and-Play Gaze Adaptation (PnP-GA) framework is an ensemble of networks that learn collaboratively with the guidance of outliers.
Since our proposed framework does not require ground-truth labels in the target domain, the existing gaze estimation networks can be directly plugged into PnP-GA and generalize the algorithms to new domains.
Motivation
Due to the differences of subjects, background environments, and illuminations between these datasets, the performance of gaze estimation models that are trained on a single dataset usually dramatically degrades when testing on a new dataset.

Differences among the domain adaptation approaches.
Unlike most of the existing works in gaze domain adaptation following supervised learning paradigm, this work aims to generalize the gaze estimation in an unsupervised manner. The above table shows the differences between the existing gaze domain adaptation approaches and UDA.
Our PnP-GA method provides an novel unsupervised domain adaptation architecture for gaze estimation.
What is PnP-GA
Our paper describes a UDA framework for gaze estimation. To be specific, we propose an outlier-guided plug-andplay collaborative learning framework for generalizing gaze estimation with unsupervised domain adaptation.
Overview of the proposed Plug-and-Play (PnP) adaption framework for generalizing gaze estimation to a new domain.
PnP-GA has several good properties:
- PnP-GA is model agnostic. Existing gaze estimation networks can be easily plugged into our framework without modification of their architectures.
- It only requires a few samples from the target domain without any labels.
- An outlier-guided loss is specifically designed to better characterize the outliers and guide the learning.
- The PnP-GA framework shows exceptional performances with plugging of the existing gaze estimation networks across different domains.
How does PnP-GA work?
Our key idea is to guide the learning by the prediction outliers, which is generated by a group of members.
Illustration of unsupervised domain adaptation for gaze estimation.
As illustrated in the figure below, at first, a group of pre-trained models (with members' number = H) are plugged into our PnP-GA. The architecture of PnP-GA is illustrated in the dark dashed box. Then a few samples from the source domain and the target domain are used for adaptation. In the next, our PnP-GA collaboratively learns from both domains. During adaptation, an outlier-guided loss is proposed to better characterize the property of outliers. After adaptation, the first member of the model group is used as an adapted model, which achieves a better performance in the target domain.
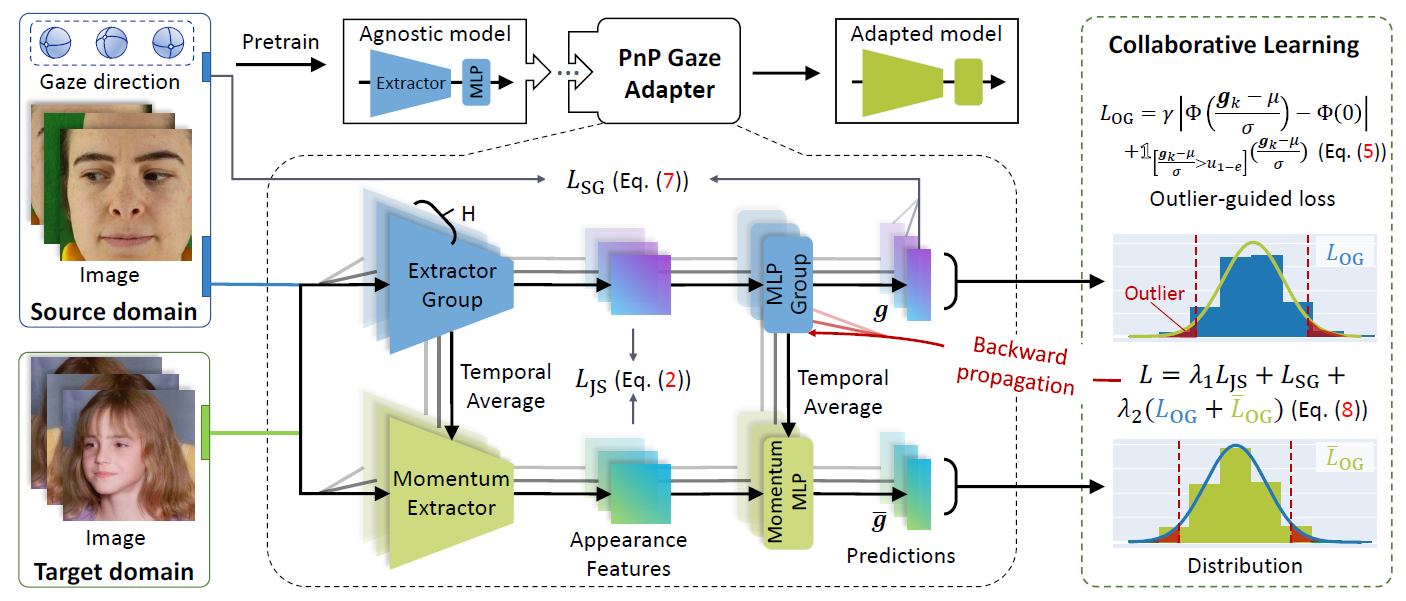
The proposed architecture.
Results
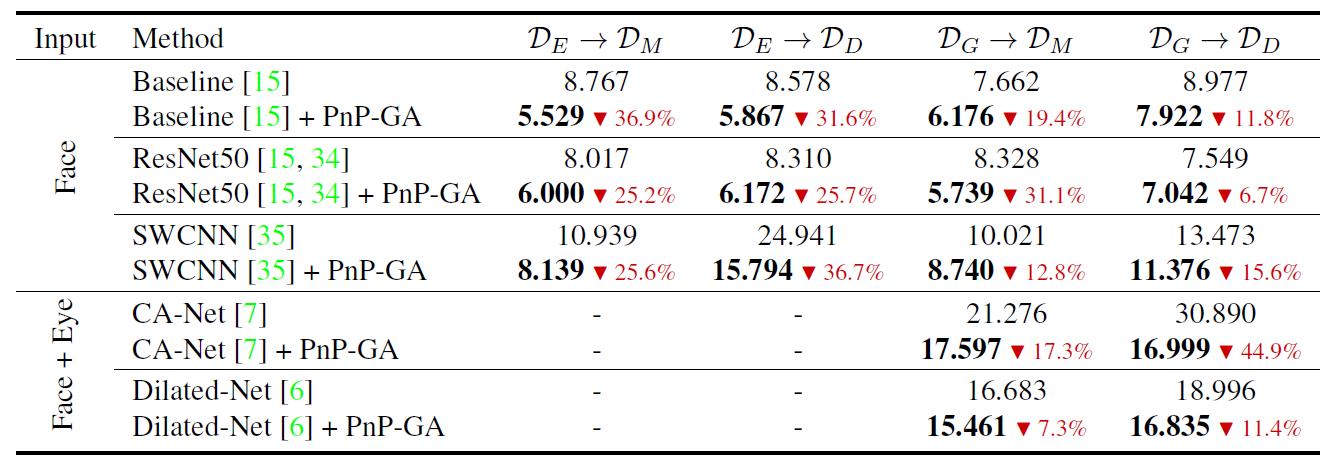
Numerical results. Domain adaptation results of plugging the existing gaze estimation networks into the proposed PnP-GA framework. Angular gaze error (degree) is used as evaluation metric.
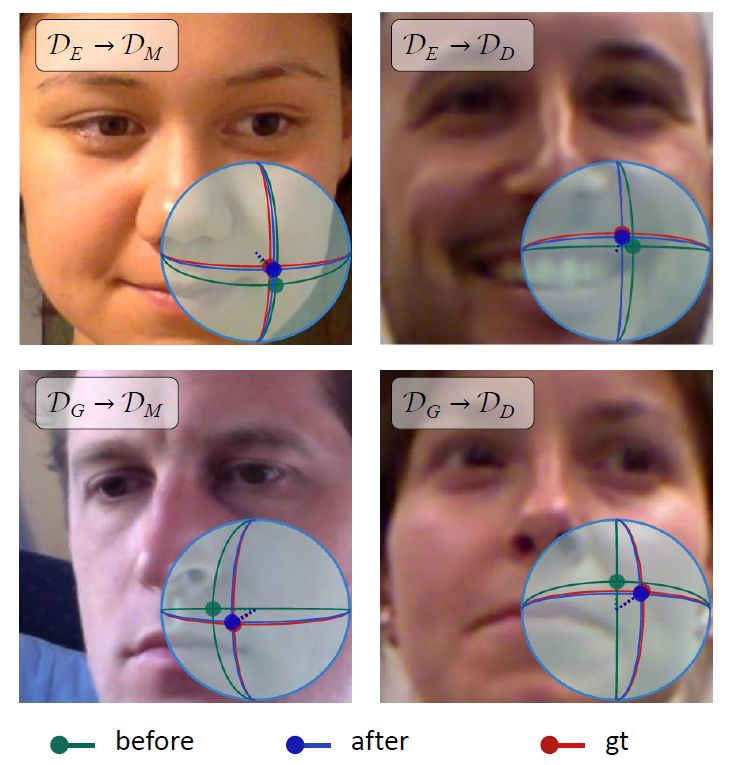
Visual results. Visual results example of estimated 3D gaze. Red points represent the ground-truth gaze direction, green and blue points represent the predictions before and after adaptation, respectively.
How to cite
Bibtex
@inproceedings{liu2021PnP_GA,
title={Generalizing Gaze Estimation with Outlier-guided Collaborative Adaptation},
author={Liu, Yunfei and Liu, Ruicong and Wang, Haofei and Lu, Feng},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision},
year={2021}
}
Acknowledgments: This work is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant 61972012 and Grant 61732016, and Baidu academic collaboration program.